ProcessMIX User Guide
Nodes
Overview
Every Flow is made of nodes, and every node contains its unique logic. All nodes are located on the Node panel. Node settings depend on the node type and are available by clicking on the node.
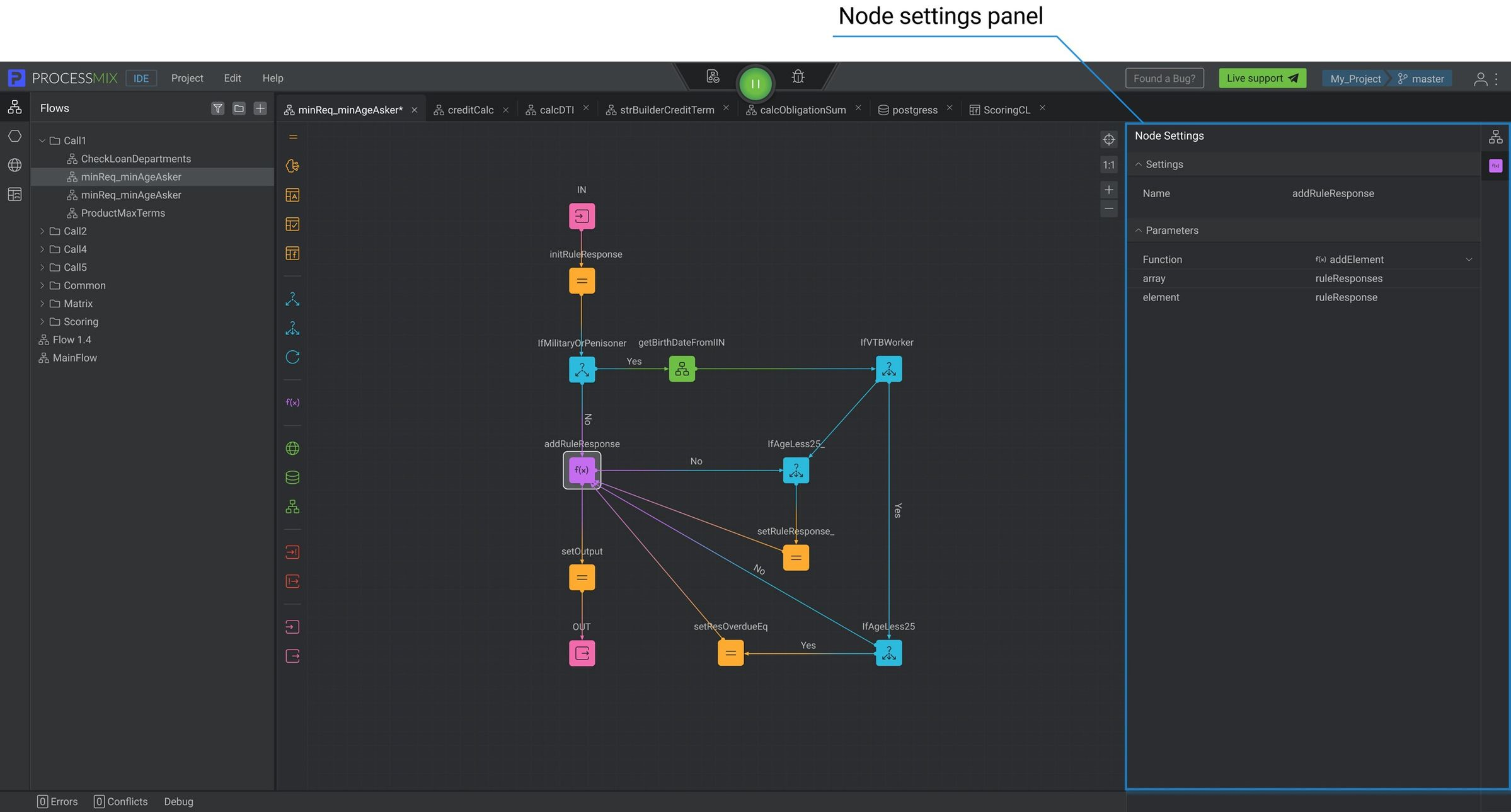
How to use Node settings to build flow?
Note:
The names of nodes within the same flow must not be the same.
List of nodes that are available to add:
| Node | Icon | Description | Settings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assign |  | A container that is used to pass values to variables. | Name — default name – Assign. Available for editing. Parameters: Variable — add a variable that has already been created before. To select the necessary variable, the Variable selector is used. In this, the created local variables, incoming and outgoing data, and node variables are available. Assign — assign a specific value to the added variable. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit values. It can be either a specific value or an expression of any complexity using existing variables, as well as outgoing node data (node variables). There can be any number of variable-assign blocks, depending on the requirements. |
| IF |  | Logic branching block. Accepts a condition and returns a boolean value. | Name — default name – If. Available for editing. Parameters: Condition — add a condition that will determine the further progress of the flow. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit conditions. If the condition is met, then further execution will go along the ‘YES’ branch. |
| Switch |  | Branch block. Accepts a condition and returns a boolean value. Unlimited number of ways. Execute the first “true”. | Name — default name – Switch. Available for editing. Parameters: Label — name of the condition. Condition — add a condition that will determine the further progress of the flow. Unlike IF, there can be several branches here, further execution will follow the first branch that meets the specified condition. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit conditions. There can be any number of label-condition blocks, depending on the requirements. |
| Iterator |  | Loop block. Iterates over the entire array. | Name — default name – Iterator. Available for editing. Parameters: List — add the list of entities that the Iterator should iterate over. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit a list. By connecting the outgoing arrow of the Iterator to the target node, where certain conditions will be checked, or certain values will be collected into a new structure for subsequent manipulations. There are no restrictions on the use of subsequent nodes or on the group of nodes involved in the iterator logic. An array is expected as input to the iterator. An iterator node must be cyclically connected to another node or group of nodes. In the node following the iterator, it becomes possible to work with the current element of the array. |
| Function Call |  | A call block for a built-in or user-created function. | Name — default name – FunctionCall. Available for editing. Parameters: Function — add the function to be called. The set of required parameters depends on the selected function. To learn about the operation of the function and the set of required parameters and types of variables that the function takes as input, use the Function selector. To get to the Function Selector, click on See all in the drop-down list of the Function field. Outgoing data also depends on the selected function. Depending on the selected function, a new variable may appear, or the same object with a modified value may be returned. To learn more about all available functions see the Expression Editor section. |
| Subflow |  | An entry point to an additional flow. Returns the result of an additional flow. | Name — default name – SubFlow. Available for editing. Parameters: Flow — add a flow that you will use. The set of required inputs depends on the selected flow as an output. |
| REST |  | Get data from external systems and services using REST connectors. It is possible to add cookies and headers, if required. | Name — default name – RestConnector. Available for editing. Parameters: Service — connect the REST service to a node for execution in a flow. Services are available from the drop down menu or through the Service selector. To get to the Service Selector, click See All in the drop-down menu of the Service field. The Service Selector displays the services of the REST connectors. The set of required request and path parameters depends on the selected service. It is necessary to define certain variables according to the logic and the corresponding type. Outgoing data depends on the method and on the established output structure in the corresponding connector service. Cookies and Headers are not required parameters in the connector. Cookies — If cookies are required to connect to the required remote service, you can set them here. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit cookies. It expects an array of cookies, the easiest way to pass values to it is to send it as input to the flow itself or assign values to the elements of the array using an iterator and the Assign node. To create an array of cookies, you must use the Structure Builder in the Structure Selector when assigning a type to a variable or property. Headers — If headers are required to connect to the required remote service, you can set them here. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit headers. It expects an array of headers. Use the same approach as for cookies. To read more, please review the Structure selector. |
| SOAP |  | Get data from external systems and services using SOAP connectors. It is possible to add cookies and headers, if required. | Name — default name – SoapConnector. Available for editing. Parameters: Service — connect the SOAP service to a node for execution in a flow. Services are available from the drop down menu or through the Service selector. To get to the Service Selector, click See All in the drop-down menu of the Service field. The Service Selector displays the services of the SOAP connectors. The set of required request and path parameters depends on the selected service. It is necessary to define certain variables according to the logic and the corresponding type. Cookies and Headers are not required parameters in the connector. Cookies — If cookies are required to connect to the required remote service, you can set them here. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit cookies. It expects an array of cookies, the easiest way to pass values to it is to send it as input to the flow itself or assign values to the elements of the array using an iterator and the Assign node. To create an array of cookies, you must use the Structure Builder in the Structure Selector when assigning a type to a variable or property. Headers — If headers are required to connect to the required remote service, you can set them here. The Expression Editor is used to add and edit headers. It expects an array of headers. Use the same approach as for cookies. To read more, please review the Structure selector. |
| S3 |  | Get data from Simple Storage Service (S3) using the S3 connector. | Name — default name – S3. Available for editing. Parameters: Connector — add a S3 Connector that has been already created before in the S3 Connector builder. Function — select a function from the list. |
| DB |  | Get data from external databases. Support PostgreSQL or MS SQL databases. Each node executes a selected query. | Name — default name – DbConnector. Available for editing. Parameters: Query — connect DB query to a node for execution in a flow. Query are available from the drop down menu or through the Query selector. To get to the Query Selector, click See All in the drop-down menu of the Query field. The Query Selector displays the queries of the DB connectors. The set of required parameters depends on the selected query. It is necessary to define certain variables according to the logic and the corresponding type. Outgoing data depends on the established output structure in the corresponding connector query. |
| Transaction Begin |  | Combines operations into one atomic package – a transaction. Opens a transaction and generates a transaction structure. | Name — default name – dbTransaction. Available for editing. Parameters: DB Сonnector — add a DB сonnector that has already been created before. |
| Transaction Commit |  | Сonfirms all changes made inside the transaction. Used to apply changes to the database, to the exact same database where the transaction was opened. | Name — default name – commitTransaction. Available for editing. Parameters: Transaction – select the variable which was created by node “Begin transaction”. It is necessary to choose exactly the structure that corresponds to the opening of the transaction (Begin transaction node) |
| Transaction Rollback |  | Сancel all changes made by the transaction. Used to cancel each operation included in the transaction to the database selected to open this transaction. | Name — default name – rollbackTransaction. Available for editing. Parameters: Transaction – select the variable which was created by the node “Begin transaction“. It is necessary to choose exactly the structure that corresponds to the opening of the transaction Begin transaction), |
| Services |  | Get data from the Ethereum blockchain network using EVM blockchain connector | Name — default name – BlockchainEvm. Available for editing. Parameters: Connector — add a Blockchain EVM connector that has been already created before in the Blockchain EVM Connector builder. Function — select from a list of existing functions. |
| Contract |  | Get data from the Ethereum blockchain network according to the chosen smart contract function. | Name — default name – BlockchainEvmContract. Available for editing. Parameters: Smart contract function — select from a list of existing smart contract’s structure functions (automatically created from an uploaded ABI contract file during the EVM Blockchain connector creation process). request – add a request to the selected smart contract function using the Expression Editor window that opens. |
| PMML |  | A way to describe predictive models generated by data mining and machine learning algorithms. | Name — default name – PMML. Available for editing. Parameters: PMML — add a specific PMML to the node that was created within the project for use in the current flow. The set of required inputs depends on the selected PMML model as an output. |
| Dictionary |  | Structured ordered data storage. It is used both in scorecards and independently in flows. | Name — default name – Dictionary. Available for editing. Parameters: Dictionary — add a specific dictionary to the node that was created within the project for use in the current flow. The set of required inputs depends on the selected dictionary model as an output. |
| Decision Table |  | Model views with complex logic. Establishes a relationship between conditions and actions. | Name — default name – DecisionTable. Available for editing. Parameters: Decision Table — add a specific decision table to the node that was created within the project for use in the current flow. The set of required inputs depends on the selected decision table model as an output. |
| ScoreCard |  | A graphical representation of a mathematical formula that is used to predict the future behavior of a customer or prospect based on what is known about them. | Name — default name – Scorecard. Available for editing. Parameters: Scorecard — select a specific scorecard to the node that was created within the project for use in the current flow. The set of required inputs depends on the selected scorecard model as an output. |
| Exception Handler |  | Process an alternative flow to handle exceptional situations. Added along with the OUT node where the result is passed. | Name — default name – ExceptionHandler. Available for editing. Parameters: Exception — select the required Exception. Depending on the selected structure, a certain Raise Exception will be processed. Each Exception Handler matches only one exception used in the Raise Exception node. Unlike Raise Exception, where values are passed to exception parameters, it forms an object containing all exception parameters and their values. |
| Raise Exception |   | Raises the specific exception. Flow can contain more than one Raise Exception node. | Name — default name – RaiseException. Available for editing. Parameters: Exception — select the required Exception, if necessary, it is possible to create a structure by inheriting the Exception superclass and adding additional properties to it. Message — add the message you want to send. It is possible to use a text message in combination with passed variable values using the concat() function. Any functions of the Expression Editor are also available for use.Can be used without an Exception Handler. |
| IN |  | Starting point of the flow. Only one is allowed. | Name — default name – IN. Available for editing. The structures for the IN node are defined in the settings of the flow itself as Input structures. Several input structures can be specified, depending on the requirements. |
| OUT |  | The ending point of the flow. There can be one or more OUTs. | Name — default name – OUT. Available for editing. The structure for the OUT node is defined in the settings of the flow itself as an Output structure. Only one output structure can be specified, but it can be of any complexity, pre-created as a custom structure through the structure builder. |
 Visual Development
Visual Development Assignment of risk level and customer category within KYC processes at customer onboarding
Assignment of risk level and customer category within KYC processes at customer onboarding Cross-Sell Offer Calculation for the 12M Client Base
Cross-Sell Offer Calculation for the 12M Client Base