
AI in Finance Field
AI nowadays becomes an essential tool to help compute and process huge amounts of data, analyze it afterward, and make a consequence on all of the meaningful data. The financial services industry undergoes rapid transformation through artificial intelligence which delivers quick and precise analytical capabilities for better decision-making. AI serves as a strong tool for improving operational efficiency and stability in the financial system. The Committee's message underscores the importance of responsible adoption of AI technology to achieve the greatest benefits toward creating stability and helping with prosperity. 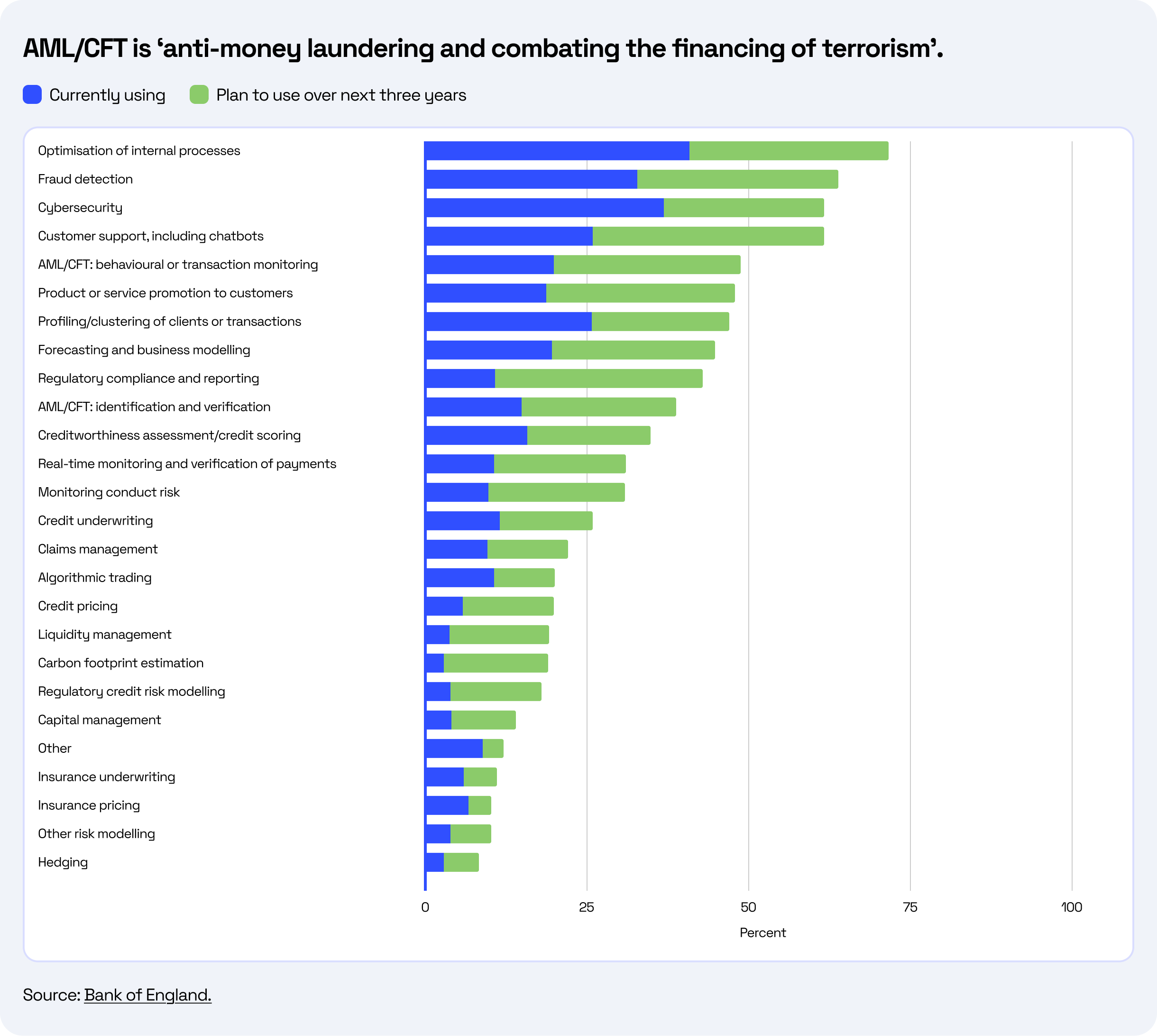

The Changing Landscape of Credit Risk
Credit risk is still one of the most important problems for banks as it impacts their potential for portfolio stability, capital, and profitability. Over the last few decades, traditional credit scoring approaches to predictive accuracy have been marginally improved through machine learning (ML) algorithms. Both approaches still remain weak in terms of interpretability, requiring structured data, or simply found difficult to apply to unstructured or higher-dimensional variables like ESG disclosures or climate change financial reports. GenAI tools can read annual reports, evaluate ESG compliance, and summarize extensive regulatory documents in a fraction of the time it would take human teams. The purpose of this paper is to explore real-world applications of GenAI in credit risk management, examine the obstacles to scaling adoption, and evaluate the strategic and regulatory implications of integrating these advanced AI technologies into banking operations. Source: McKinsey, Embracing Generative AI in Credit Risk, 2024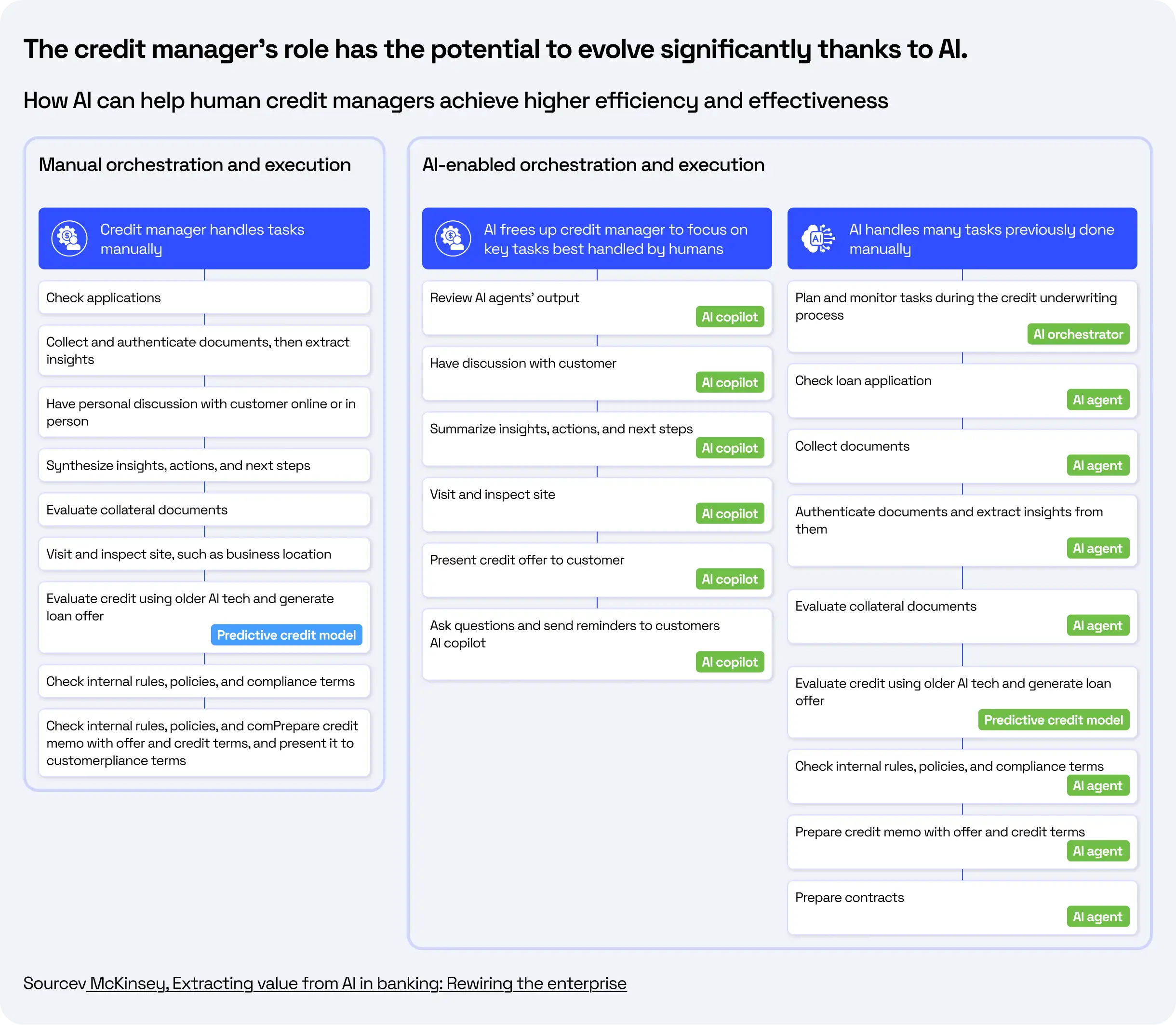
Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations
Over the last decades, ML-based credit scoring models (e.g., logistic regression, decision trees, gradient boosting) have become the industry standard. Applications include:- Default prediction based on historical repayment behavior and demographic features.
- Fraud detection through anomaly detection and transaction monitoring.
- Portfolio risk assessment via statistical stress-testing and macroeconomic scenario analysis.
- Dependence on structured, labeled datasets — difficult to scale when new, text-heavy regulations (e.g., ESG) emerge.
- Limited interpretability, raising fairness and explainability concerns.
- Inability to process unstructured data at scale (contracts, PDFs, customer communications).
- Vulnerability to bias, replicating inequalities from historical data.
The Emergence of Generative AI in Credit Risk
Generative AI introduces capabilities far beyond traditional ML:- Processing unstructured data (ESG reports, climate disclosures, legal documents).
- Multi-step automation (data extraction, validation, summarization, and drafting of credit memos).
- Contextual reasoning with dialogue-based interfaces for analysts and risk officers.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): trained on vast corpora and able to understand complex financial or regulatory text.
- Agentic AI systems: multi-agent setups where different agents handle extraction, validation, and simulation tasks — reducing hallucinations and error propagation.

Case Studies: Early Applications in Banks
Credit Memo Drafting
Banks report time savings of 30–50% when LLMs automatically extract borrower data, analyze statements, and draft memos. Source: McKinsey & IACPM, 2025UK High Street Bank: Comparing Machine Learning and Traditional Credit Scoring
A prominent UK high street bank recently conducted an experiment to compare the effectiveness of machine learning with traditional credit scoring methods in predicting loan defaults. Thanks to its state-of-the-art technology, Kortical was able to build thousands of machine learning models and identify 83% of previously unseen potential bad debts, at the same rejection rate. The machine learning process enabled the bank to discover otherwise hidden behaviors in consumer conduct, which has subsequently improved outcomes, reduced likelihood of default, and secured a quicker model build outcome. Source: KorticalChinese Commercial Bank: Using LightGBM and SMOTEENN for Credit Risk Assessment
A Chinese bank used LightGBM with SMOTEENN to improve credit risk predictions. Dimensionality reduction like PCA boosted accuracy over traditional models and helped identify creditworthy clients.This approach processed structured and partially unstructured data, enabling better decisions, lower default risk, and more efficient portfolio management. Source: arXivPortfolio Monitoring and Early Warning
GenAI is used for early warning signals by scanning unstructured news, filings, and reports for risk factors. Source: McKinsey & IACPM, 2025Challenges and Risks in Scaling GenAI
Significant hurdles will have to be cleared if scaling GenAI is to stand the same potential as its pilots:
- Explainability & Fairness: LLMs being “black boxes” will always lead to ethical and regulatory issues.
Source: FSB, How Regulators Can Address AI Explainability, 2024 - Integrating external foundation models poses the risk of sharing sensitive data, necessitating thorough analysis and careful implementation of integrations. Source: McKinsey, How Generative AI Can Help Banks Manage Risk and Compliance, 2024
- A significant challenge facing the banking sector is the shortage of talent skilled in General Artificial Intelligence (GenAI).
According to a recent survey, a striking 67% of banks report being unable to find enough qualified professionals to meet their GenAI needs.
This talent gap is becoming increasingly pressing as the financial industry continues to adopt advanced technologies.
Source: McKinsey & IACPM, 2025
Developing a GenAI Ecosystem for Credit Risk Management
- Transitioning from proofs of concept to enterprise-wide implementation necessitates organizational change. McKinsey has identified eight best practices.
Source: McKinsey & IACPM, 2025 - Roadmap for AI capabilities aligned to business strategy.
- A hybrid-cloud infrastructure that is secure and scalable.
- Utilization of foundation models (e.g., GPT, Llama, Claude).
- Open-source libraries that can be reused to accelerate the development life cycle.
- MLOps pipelines for continuous monitoring and updates.
- Robust governance structures used for responsible AI.
- Centers of Excellence (CoE) help build institutional knowledge.
- A modular architecture separating user experience, business logic, and infrastructure.
Regulatory and Strategic Implications: Regulators are actively shaping the AI credit risk landscape:
- The Bank of England warns that AI use in financial services induces systemic risks like bias, as well as reliance on vendors or risk exposure to model instability.
Source: Bank of England, Financial Stability in Focus: Artificial Intelligence in the Financial System, April 2025 - The BIS and FSB emphasize governance frameworks and the requirement of banks to demonstrate a balance of innovation and explainability.
Source: BIS/FSB, 2024 - The ECB also provides supervisors with secondary guidance on climate stress testing and directs banks to use AI-driven text mining for ESG reporting.
Source: BIS, Climate-related Financial Risks, 2023
Conclusion
Generative AI technology has moved from theoretical development to actual operational use in banking systems. Leading global banks have already integrated AI into their operations, and most plan to expand its use further in the near future. The financial sector uses Generative AI to generate credit memos and conduct ESG research and manage investment portfolios according. The upcoming stage requires institutions to expand their adoption of the technology with the implementation of governance systems and data quality management and regulatory compliance measures. Those banks which treat a strategic approach on early implementation would have faster operations with precise results, and regulatory compliance. The financial industry will fully adopt GenAI as its standard for credit risk management during the period from 2025 to 2028.



